Deciphering the Airborne Sounds of Plants Under Drought Stress
Abstract:
Bibliography/Citations:
Hadany, L., et al. "Plants emit informative airborne sounds under stress." biorXiv, doi:10.1101/507590.
Laschimke, R., Burger, M., & Vallen, H. "Acoustic emission analysis and experiments with physical model systems reveal a peculiar nature of the xylem tension." Journal of Plant Physiology, vol. 163, 2006, pp. 996-1007.
Jingmin, L., Chong, L., Zheng, X., Zhang, K., Ke, X. "A Microfluidic Pump/Valve Inspired by Xylem Embolism and Transpiration in Plants." PLOS ONE, November 2012.
Laschimke, Ralf, Maria Burger, and Hartmut Vallen. "Acoustic emission analysis and experiments with physical model systems reveal a peculiar nature of the xylem tension." Journal of Plant Physiology, vol. 163, 2006, pp. 996-1007, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2006.05.004.
Cavitation and Embolism in Vascular Plants (With Diagram)." Biology Discussion, https://www.biologydiscussion.com/plants/cavitation-and-embolism-in-vascular-plants-with-diagram/22732.
Baldwin IT, Halitschke R, Paschold A, von Dahl CC, Preston CA. Volatile signaling in plant-plant interactions: "talking trees " in the genomics era. science. 2006;311:812-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1118446.
Dutta, S., Chen, Z., Kaiser, E., Matamoros, P. M., Steeneken, P. G., & Verbiest, G. J. (2022). Ultrasound pulse emission spectroscopy method to characterize xylem conduits in plant stems. research.
Gilbert, L., & Johnson, D. (2017). Plant-plant communication through common mycorrhizal networks. in Advances in botanical research (Vol. 82, pp. 83-97). Academic Press.
Ghosh, R., Mishra, R. C., Choi, B., Kwon, Y. S., Bae, D. W., Park, S. C., ... & Bae, H. (2016). Exposure to sound vibrations lead to transcriptomic, proteomic and hormonal changes in Arabidopsis. scientific reports, 6(1), 33370.
Haswell, E. S., Phillips, R., & Rees, D. C. (2011). Mechanosensitive channels: what can they do and how do they do it? Structure, 19(10), 1356-1369.
Heffner, H. E., & Heffner, R. S. (2007). Hearing ranges of laboratory animals. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science, 46(1), 20-22.
Joshi, J., Stocker, B. D., Hofhansl, F., Zhou, S., Dieckmann, U., & Prentice, I. C. (2022). Towards a unified theory of plant photosynthesis and hydraulics. Nature Plants, 8(11), 1304-1316.
Website: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41477-022-01244-5
Khait, I., Lewin-Epstein, O., Sharon, R., Saban, K., Perelman, R., Boonman, A., ... & Hadany, L. (2018). Plants emit informative airborne sounds under stress. biorxiv, 507590.
Website: https://www.sci.news/biology/plants-ultrasonic-clicks-07895.html
Khait, I., Lewin-Epstein, O., Sharon, R., Saban, K., Goldstein, R., Anikster, Y., ... & Hadany, L. (2023). Sounds emitted by plants under stress are airborne and informative. cell, 186(7), 1328-1336.
McElrone, A. J., Choat, B., Gambetta, G. A., & Brodersen, C. R. (2013). Water uptake and transport in vascular plants. Nature Education Knowledge, 4(5), 6.
M. Zhang and J. H. M. Willison, "Electrical impedance analysis in plant tissues: the effect of freeze-thaw injury on the electrical properties of potato tuber and carrot root tissues," Canadian Journal of Plant Science, vol. 72, pp. 545-553, 1992.
Oda, S., Sakaguchi, M., Yang, X., Liu, Q., Iwasaki, K., & Nishibayashi, K. (2021). Ultrasonic treatment suppresses ethylene signaling and prolongs the freshness of spinach. Food Chemistry: Molecular Sciences, 2, 100026.
Ponomarenko, A., Vincent, O., Pietriga, A., Cochard, H., Badel, É., & Marmottant, P. (2014). Ultrasonic emissions reveal individual cavitation bubbles in water-stressed wood. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 11(99), 20140480.
Rafał Chudy, 2016, Trees call for water when they are thirsty.
Website: https://www.forest-monitor.com/en/trees-call-for-water-when-they-are-thirsty/
Y.Z. Lin, 1982, Research on the new technology of stomatal opening and closing and its application, National Elementary and Middle School Science Exhibition, Biology First Place, Taiwan Network Science Museum
Website: https://www.ntsec.edu.tw/science/detail.aspx?a=21&cat=7128&sid=7719&print=1
Chan, L. S.. (2013). Evapotranspiration in the growing environment of crops. Special issue of Taichung Agricultural Improvement Center, 109-114.
Website: https://www.tcdares.gov.tw/upload/tdais/files/web_structure/8187/TC0211619.pdf
Yim Hongyang, 2013, Biological Signal Communication Pipeline - The Negative Effect of Human Interference, Science and Technology Grand Park
Website: https://scitechvista.nat.gov.tw/Article/C000009/detail?ID=ec4fb250-6b40-4c0d-9910-dee8a9e8fec8
Additional Project Information
Research Plan:
Research Plan: Ultrasonic Emissions of Plants Under Drought Stress
Rationale:
With global water resources under increasing pressure, there's a pressing need for sustainable agricultural practices that optimize water usage. Recent research suggests that plants emit differentiated airborne sounds under stress conditions like drought, potentially signaling their hydration needs. This study aims to delve into the ultrasonic emission characteristics of plants under different hydration levels, exploring the possibility that these signals might not only indicate plant water stress but also influence the physiological responses of surrounding plants. This research could revolutionize irrigation practices, leading to more efficient water use in agriculture.
Hypothesis:
I hypothesized that plants emit distinct airborne sounds in response to drought stress compared to when adequately watered.
Research Questions
1. How do the airborne sounds of plants vary between well-watered and drought conditions?
2. Can airborne sounds from drought-stressed plants trigger physiological changes in neighboring plants?
3. How can the understanding of plant airborne sounds under drought stress inform the development of precision irrigation systems that cater to the specific hydration needs of plants?
Procedures:
1) Experimental Setup:
a. Use Ixora plants as the primary subjects for experimentation.
b. Use the SONAPHONE ultrasonic testing device and analysis software for detecting and analyzing ultrasonic emissions/ plant airborne sounds.
c. Design experiments to compare ultrasonic signals/airborne sounds while watered and drought conditions.
2) Data Collection and Analysis:
a. Record plant airborne sounds 1 hour and 9 hours after watered, 10 minutes each time.
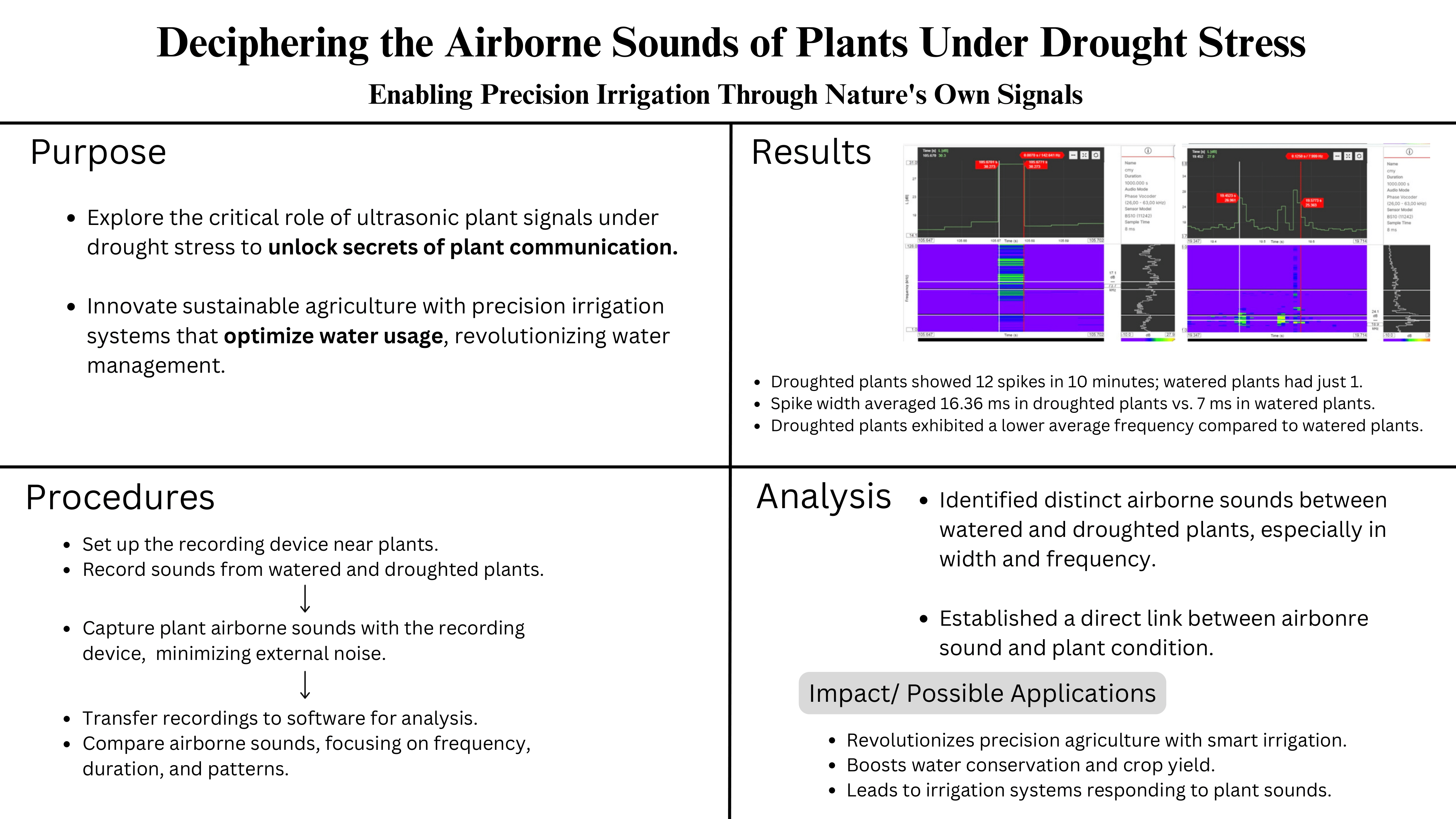
b. Analyze the data to identify differences between droughted and watered plants’ ultrasonic emission/airborne sounds such as their sound level, frequency, and number of occurrences.